SORMAS Overview
Summary
SORMAS is a comprehensive surveillance, management, and analysis tool for infectious diseases that enables countries to monitor and control outbreaks effectively. With SORMAS, public health officials can track infection rates, manage cases and contacts, and access real-time statistics and data visualizations.
This powerful tool is designed to work seamlessly across a range of devices, including desktop computers, tablets, and mobile phones. Whether online or offline, users can access 10 different menus, each tailored to specific needs, such as case management, contact tracing, and task scheduling. The intuitive dashboard provides a centralized view of key data and statistics, making it easy to identify trends and track progress over time.
SORMAS is built to ensure data privacy and security, with different user roles and permissions to protect sensitive information. It also facilitates seamless communication and coordination among different public health institutes, such as hospitals, labs, and surveillance officers, streamlining workflows and enhancing collaboration.
Ownership
SORMAS is available to countries for use and it is customizable to country specific needs in conformance to their surveillance systems and structures.
Data processed through SORMAS belongs to the countries and its hosting and management are the responsibility of their authorities.
Security
The SORMAS data protection and security concept follows the European data protection regulations (GDPR). It includes anonymization, pseudonymization and data deletion, subject to countries. In addition, regular data and system security measures are applied. Furthermore, the system is only accessed according to user rights defined by countries.
Transparency
As an open source software, SORMAS ‘s source code is publicly available on the GitHub platform. It is licensed under the GNU General Public License 3.0. which makes sure that changes to the codebase or derivate projects have to be made publicly available as well.
The development process is transparent and collaborative. This way, countries enjoy high quality software and avoid vendor lock in.
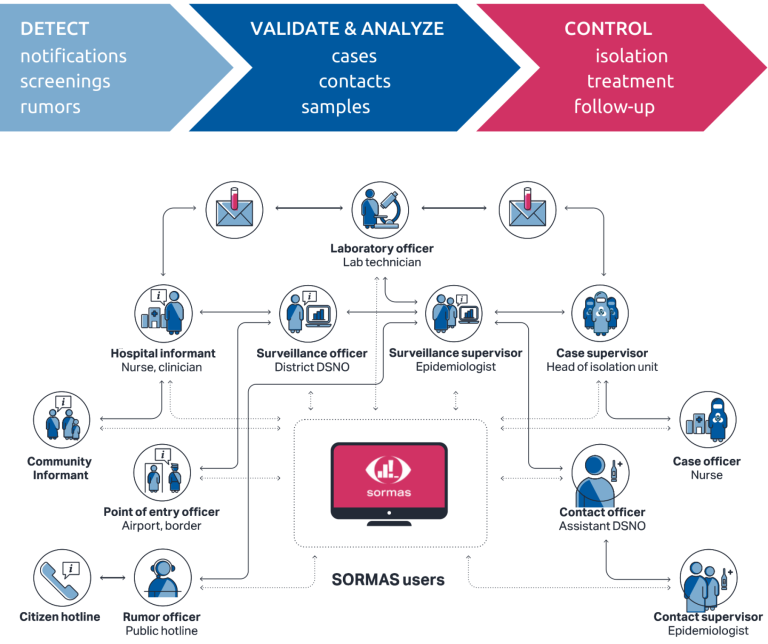
How it works
A collaborative platform for early warning, detection and response to outbreaks!
Real-time, multidirectional data sharing with integrated task management that enables efficient coordination and structured communication.
SORMAS is a Digital Public Good

Endorsed by the UN Secretary General’s Roadmap for Digital Cooperation, the Digital Public Goods are:
“open source software, open data, open AI models, open standards and open content that adhere to privacy and other applicable laws and best practices, do no harm, and help attain the SDGs.”
SORMAS also supports the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goal Nr. 3 as defined by the United Nations.


SORMAS is a Mature Global Good
A mature digital health software global good is software that is free and open source, is supported by a strong community, has a clear governance structure, is funded by multiple sources, has been deployed at significant scale, is used across multiple countries, has demonstrated effectiveness, is designed to be interoperable and is an emergent standard application.
History
SORMAS has been developed during the Ebola epidemic in West Africa in 2014 and was first deployed in Nigeria in 2015, followed by Ghana a few years later.
In the meantime SORMAS became open-source to ensure a sustainability and independence from IT companies.
Due to the coronavirus pandemic SORMAS was developed further and is now used in several countries in Africa, Asia and Europa.

After the Ebola epidemic in West Africa in 2014/2015, a consortium of German and Nigerian public health and research institutions and a software company, coordinated by the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research (HZI), developed the Surveillance Outbreak Response Management and Analysis System (SORMAS). After the SORMAS prototype was developed, it was tested at different health system levels in two states of Nigeria.
2015In early 2020, a COVID-19 module was quickly developed in SORMAS, which led to its adoption by countries like France, Switzerland, Fiji, Ivory Coast, Nepal, and Germany. The same year, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and the OCEAC (Organisation de Coordination pour la lutte contre les Endémies en Afrique Centrale) also decided to pilot SORMAS.
2020

